Curious about the energy your computer consumes?
You’re not alone! Many of us keep our digital companions running for hours without considering the impact on our electricity bills.
A standard desktop might use surprisingly different amounts of power compared to a lightweight laptop. And those high-performance gaming systems?
They can consume electricity at rates that might make you think twice about those all-night gaming sessions.
In this guide, we’ll examine exactly how much power various computers use over a full day, what factors influence consumption, and how to calculate the actual cost to your wallet.
Plus, you’ll learn practical ways to reduce your computer’s energy usage without sacrificing performance.
Factors That Affect a Computer’s Electricity Consumption
1. Type of Computer (Desktop vs. Laptop)
|
Computer Type |
Average Power Consumption |
Key Characteristics |
|
Desktop |
60-250W |
• Higher performance components • Constant AC power • Multiple internal components • Better cooling systems |
|
Laptop |
15-60W |
• Power-optimized components • Battery + AC operation • Integrated display • Compact cooling systems |
|
All-in-One |
30-100W |
• Integrated monitor • Desktop components in compact form • Less expandability |
|
Mini PC |
10-35W |
• Smaller, mobile-grade components • Limited expansion options • Compact size |
2. Hardware Specifications
- CPU and GPU power draw: Central processing units can consume anywhere from 15W (efficient laptops) to 150W+ (high-performance desktops).
Graphics processing units range even more dramatically, from 5W integrated solutions to 450W for top gaming/professional cards. These two components often account for the majority of a computer’s power consumption.
- RAM and storage considerations: Memory modules typically use 2-5W per stick regardless of capacity.
Traditional hard drives consume 6- 9W while actively spinning, but solid-state drives use just 2- 3W with no moving parts, making them more energy-efficient while offering better performance.
3. Peripheral Devices
- Monitors, printers, external drives: External displays add 20- 100W, depending on size and technology (LED uses less than older LCD).
Printers consume minimal power when idle but spike to 30- 500W while printing.
External hard drives typically draw 5- 10W when active, while USB flash drives use under 1W.
Power Supply Efficiency
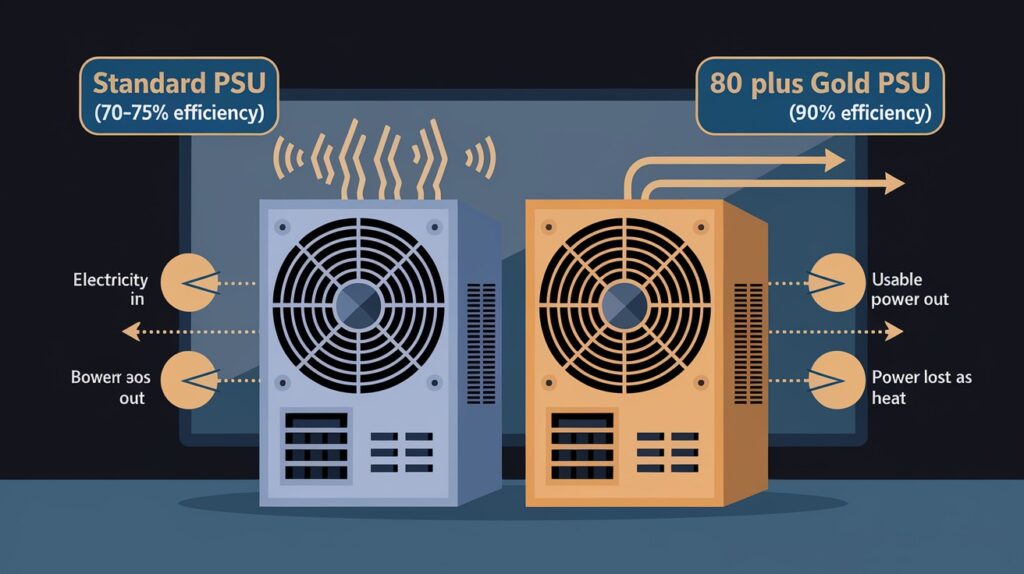
Power supply units convert AC power from the wall into DC power that components can use. Efficiency ratings (80 Plus Bronze through Titanium) indicate how much electricity is lost as heat during conversion.
A high-quality 80 Plus Gold PSU (90% efficient) wastes significantly less power than standard units (70-75% efficient), especially important for systems running continuously.
How to Calculate Computer Power Usage Over 24 Hours?
1. Understanding Watts and Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
Watts (W) measure the rate of energy consumption at any given moment, similar to how fast water flows through a pipe. A computer drawing 100W is using 100 watts of power right now.
Kilowatt-hours (kWh) measure total energy used over time, like the total volume of water that passed through the pipe. This is what your electricity bill charges for. One kilowatt-hour equals 1,000 watts used for one hour.
The distinction matters because computers rarely use constant power.
A gaming PC might draw 300W while gaming but only 50W while browsing the web, making total consumption dependent on usage patterns throughout the day.
Formula for Estimating Daily Electricity Use
- (Wattage × Hours Used) ÷ 1000 = kWh
For example:
- A desktop computer using 100W for 8 hours: (100W × 8h) ÷ 1000 = 0.8 kWh
- The same computer in sleep mode at 5W for 16 hours: (5W × 16h) ÷ 1000 = 0.08 kWh
- Total daily usage: 0.8 kWh + 0.08 kWh = 0.88 kWh
For systems with varying power draw throughout the day, calculate each usage state separately:
- Find the average wattage for each type of activity
- Multiply by hours spent in that activity
- Add all values together
- Divide by 1000 to convert to kWh
2. Using Power Meters for Accurate Measurement
Power meters provide precise measurements of actual electricity consumption, accounting for all variables, including:
- Plug-in wattmeters: Devices like Kill-A-Watt or Watts Up Pro connect between your computer and wall outlet, displaying real-time power draw and total consumption over time. Prices range from $20-$50, making them affordable tools for accurate measurement.
- Smart plugs with energy monitoring: Wi-Fi-connected smart plugs often include power monitoring features, with the added benefit of tracking usage patterns through smartphone apps and allowing remote power management.
- UPS systems with displays: Many uninterruptible power supplies show current power draw of connected equipment, though they may not track consumption over time.
- Home energy monitors: Whole-house monitoring systems can track individual circuits, useful for identifying the total consumption of your computing setup, including all peripherals.
For the most accurate results, leave a power meter connected for several days to capture your typical usage pattern, including periods of high activity, idle time, and sleep states.
Conclusion
So what’s the bottom line on your computer’s power appetite?
As we’ve seen, it varies widely based on what you’re using and how you’re using it.
That gaming rig might cost more to run than you realized, while your work laptop is probably easier on your electricity bill than your coffee maker!
Taking a few minutes to calculate your actual usage can be eye-opening.
Whether you’re budget-conscious or environmentally minded, small changes like adjusting power settings or upgrading to more efficient components can make a meaningful difference over time.
Remember, the most accurate way to know for sure is to measure with a power meter.
Give it a try, you might find that your computer is more energy-efficient than you thought, or identify opportunities to cut your electricity costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do laptops use less electricity than desktops?
Yes, laptops typically use 15- 60W while desktops consume 60-250W due to more efficient components and lower power needs.
Will using sleep mode save much electricity?
Absolutely. Sleep mode cuts power usage to just 1- 5W compared to 50-100W when idle, saving substantial energy daily.
How much does it cost to run my computer all day?
For an average desktop (100W), about $0.24-$0.36 daily at typical electricity rates of $0.10-$0.15 per kWh.