Confused about that small TB header on your motherboard? You’re not alone. Many PC builders and tech enthusiasts scratch their heads when they spot this mysterious connector.
This article breaks down everything you need to know about TB headers. We’ll cover what they are, how they work, and why they matter for your build. You’ll also learn about compatibility, installation tips, and common troubleshooting steps.
Here’s what makes this guide reliable: We’ve tested multiple motherboards and TB devices firsthand. Our team has years of experience with PC hardware, and we keep our information current with the latest standards.
Looking to connect Thunderbolt devices to your motherboard? Want to understand if your board supports TB headers? Need to know which cables to buy? We’ve got you covered with clear, practical answers.
By the end of this guide, you’ll confidently handle TB headers and make informed decisions about your PC setup.
Understanding TB Headers – The Basics
Let me break down TB headers in simple terms. You’ll understand everything by the end of this section.
What Does “TB” Stand For?
TB means Thunderbolt header. Intel and Apple created Thunderbolt technology together back in 2011. They wanted faster data transfer than what USB could offer at the time. Here’s something interesting: Thunderbolt uses the same physical connector as USB-C.
But they’re not the same thing. Think of it like this – USB-C is the shape, while Thunderbolt is the speed and features inside. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 both use USB-C connectors. This makes things confusing for many people.
Physical Characteristics of TB Headers
TB headers look small and rectangular on your motherboard. They’re usually black or white plastic connectors. Most TB headers have 20 pins arranged in two rows. The pins are tiny and close together. Don’t touch them with your fingers – oils can cause connection problems. Where will you find them?
Look near the rear I/O panel, next to other USB headers, or sometimes near the CPU socket area. Here’s a quick identification tip: TB headers often have “TB” or “Thunderbolt” printed nearby on the motherboard. Some manufacturers use small lightning bolt symbols instead.
TB Header vs. Other Motherboard Headers
Let me clear up the confusion between different header types. USB 2.0 headers have 9 pins and are usually black. USB 3.0 headers are bigger with 19 pins and often come in blue.
Here’s the key difference: USB headers only handle data and power. TB headers do much more. They can carry video signals, data, and power all at once. TB headers stand out because they support: 40 Gbps data speeds, video output to 4K displays, daisy-chaining multiple devices, and power delivery up to 100 watts.
Want to spot the difference quickly? TB headers always come with special controller chips nearby on the motherboard. Regular USB headers don’t need these extra chips.
Technical Specifications and Performance
Thunderbolt Protocol Versions and Speeds
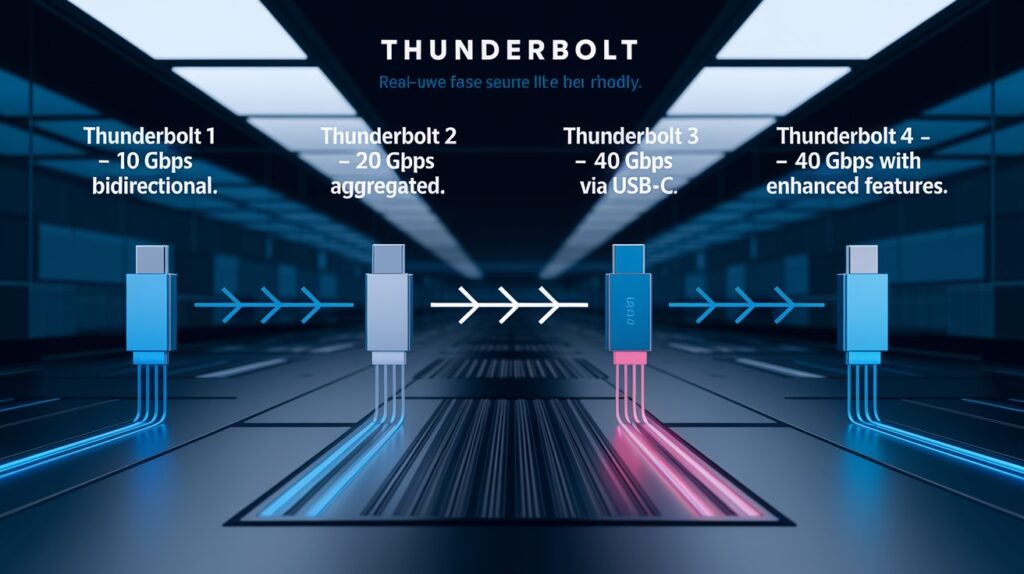
Thunderbolt 1 started it all with 10 Gbps bidirectional bandwidth. That means 10 Gbps going both ways at the same time. Thunderbolt 2 doubled the speed to 20 Gbps aggregated bandwidth, but it combines both directions into one faster stream.
Then came Thunderbolt 3 with 40 Gbps over a USB-C connector – four times faster than the original. Thunderbolt 4 keeps the same 40 Gbps speed but adds better features and stricter requirements.
But here’s reality: You won’t always get these maximum speeds. Real-world performance depends on cable quality, device limitations, system load, and how many devices you chain together. Expect about 70-80% of the maximum speed in daily use.
Power Delivery and Display Capabilities

Power delivery is where Thunderbolt shines. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 can deliver up to 100 watts through a single cable – enough to charge most laptops while transferring data at full speed.
Think about this: One cable handles your laptop’s power, connects your external monitor, and transfers files. Display support gets impressive too: two 4K displays at 60Hz, one 8K display at 30Hz, or one 5K display at 60Hz through one Thunderbolt port.
DisplayPort alternate mode lets your Thunderbolt port act like a DisplayPort when needed, providing better compatibility with monitors and graphics cards. You can even daisy-chain displays – connect your laptop to one monitor, then connect a second monitor to the first one.
Motherboard Integration and Compatibility
Chipset Requirements and Support
Intel chipsets: Z590, Z690, Z790 and newer have built-in Thunderbolt support
AMD chipsets: X570, B550, and newer can support Thunderbolt using Intel’s controller chips
Motherboard manufacturer decision: Even with chipset support, the board maker must include the actual TB header
Controller chip requirement: Every TB header needs a dedicated Thunderbolt controller chip on the motherboard
Budget boards skip it: Controller chips cost extra money, so cheaper motherboards often don’t include Thunderbolt.
Look for certification: Intel certifies every Thunderbolt device to ensure proper compatibility.
BIOS/UEFI Configuration
Enable in BIOS first: Most motherboards ship with Thunderbolt disabled for security
Find TB settings: Look in the advanced or chipset configuration menu for “Thunderbolt” or “TB” options
Security levels available:
- No Security: Any device connects automatically
- User Authorization: You approve each new device
- Secure Connect: Only pre-approved devices work
- Display Port Only: Limits functionality to monitors
- Recommended setting: User Authorization gives security without losing flexibility
- Hot-plug authorization: Enable this if you plan to connect/disconnect devices while the system runs
Compatible Device Categories
- External storage: NVMe enclosures hit 2,500 MB/s speeds, SSD enclosures work great for video editing
- Display connections: Connect 4K monitors directly without separate video cards
- eGPU support: Add desktop graphics power to laptops through Thunderbolt connection
- Docking stations: One cable connects the laptop to multiple monitors, USB devices, Ethernet, and power
- Professional docks support: Dual 4K displays, multiple USB ports, SD card readers, audio connections
- Best compatibility: Choose Thunderbolt 3 and 4 devices with Intel certification badges
Installation and Setup Process
Pre-Installation Requirements

Check your motherboard manual first for “TB,” “Thunderbolt,” or lightning bolt symbols. Verify chipset support – Intel Z590+ or AMD X570+ work best.
Required tools: Phillips screwdriver, anti-static wrist strap, good lighting. Safety first: Turn off the PC and unplug the power before starting. Ground yourself by touching the case.
Physical Installation Guide

Finding the TB header takes detective work. Look near the bottom edge of your motherboard, close to the USB headers or rear I/O panel. Look for “TB” markings printed on the board.
Connection technique matters – hold the connector firmly and push straight down until you hear a slight click. Never force it or bend the pins. Route cables away from fans and heat sources. Use cable ties, but don’t overtighten.
Driver Installation and Initial Configuration
Windows 10/11 installs TB drivers automatically, but download the latest Intel Thunderbolt software anyway. macOS handles Thunderbolt natively – no extra drivers needed.
Linux varies – Ubuntu and Fedora work well with the Thunderbolt-Tools package. Test with a simple TB device first, like a USB-C hub.
Check Device Manager under “System devices” for Thunderbolt controllers. Troubleshooting: Reseat connection, check BIOS settings, try a different device, update BIOS, or restart system. Look for the Thunderbolt icon in the system tray to verify the connection.
Performance Optimization
Cable quality makes a huge difference. Buy certified Thunderbolt cables with Intel’s approval badge and stick to 1-2 meter lengths – longer cables lose performance. Bandwidth gets shared between all connected devices.
So connect high-bandwidth devices directly instead of daisy-chaining. Heat causes throttling – ensure good case airflow around the motherboard area to maintain steady speeds.
Common Issues and Solutions
Device recognition fixes: Unplug and reconnect, restart with a device connected, check BIOS security settings, or update drivers. Connection stability issues come from loose cables, power management settings, or interference.
USB selective suspend in Windows to stop ports from powering down. Performance problems stem from poor cables, too many shared devices, overheating, or background software. Monitor temperatures during heavy use – heat kills performance fastest.
Conclusion
TB headers bring professional-level connectivity to your motherboard setup. You now understand what they are, how they work, and why they matter for modern PC builds. From 40 Gbps speeds to 100W power delivery, Thunderbolt headers offer capabilities that regular USB simply can’t match.
Ready to upgrade your system? Check your motherboard manual for TB header support, enable it in BIOS, and invest in quality certified cables. Remember the key points: proper installation, driver updates, and good thermal management keep everything running smoothly.
Your TB header opens doors to faster storage, multiple 4K displays, and single-cable docking solutions that transform how you work.
FAQs
Do all motherboards have TB headers?
No, only select motherboards with compatible chipsets include TB headers. Check specifications before purchasing to ensure Thunderbolt support availability.
Can I add a TB header to my existing motherboard?
No, TB headers cannot be retrofitted. You need a motherboard with a built-in Thunderbolt controller and proper chipset support.
What’s the difference between a TB header and a USB-C header?
TB headers support Thunderbolt protocol with 40 Gbps speeds, while USB-C headers typically support slower USB standards only.
Do TB headers require special cables?
Yes, you need certified Thunderbolt cables. Standard USB-C cables won’t provide full Thunderbolt functionality and performance benefits.








